Research Funding
None
Background
The treatment landscape for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has transformed in the past two years. Both Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab and Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib are approved regimens for first-line treatment of intermediate to poor-risk patients with advanced RCC. The choice between these immunotherapy-based combinations for first-line therapy is highly debated; no prior study has evaluated the cost-effectiveness of both combinations compared to Sunitinib.
Methods
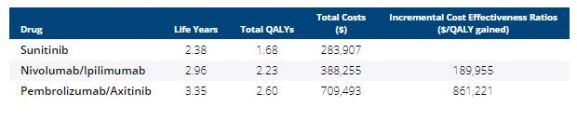
We used a decision analytic Markov model informed by the recent Checkmate-214 and Keynote-426 phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trials to evaluate costs and effectiveness of Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab, Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib, and Sunitinib in the first-line treatment of advanced RCC from a US health payer perspective. We used the model to extrapolate survival beyond the closure of the trials and examined the robustness of our findings with sensitivity analyses. Main outcomes were life expectancy, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), costs, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios, all discounted at 3% annually.
Results
Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab increased life expectancy by 0.58 years at cost of approximately $190,000 per QALY gained compared to Sunitinib. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib increased life expectancy by 0.39 years at a cost of approximately $861,000 per QALY gained compared to Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab. The results were not sensitive to reasonable changes in drug costs and quality of life estimates. Both combinations cost more than the traditional willingness-to-pay threshold (WTP) of $150,000 per QALY gained. A 20% price reduction is required for Nivolumab and Ipilimumab to be cost-effective and a 48% price reduction is required for Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib to be cost-effective.
Conclusions
Both Nivolumab plus Ipilumumab and Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib provide increased longevity and reduced morbidity relative to Sunitinib. However, the prolonged duration of treatment and doublet-drug pricing results in high-costs. Price reductions are required for both of the immunotherapy-based combinations to be cost-effective.